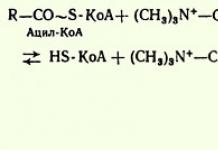
Elizabeth II (Elizabeth II) Queen of Great Britain and Northern Ireland - since February 6, 1952
Coronation: June 2, 1953
Predecessor: George VI
Heir apparent: Charles, Prince of Wales
Head of the Commonwealth of Nations
Religion: Anglicanism
Birth: 21 April 1926
London, Great Britain
Genus: Windsor dynasty
Birth name: Elizabeth Alexandra Maria
Father: George VI
Mother: Elizabeth Bowes-Lyon
Spouse: Philip Mountbatten
biography of queen elizabeth 2
Elizabeth II(English Elizabeth II), full name - Elizabeth Alexandra Mary (English Elizabeth Alexandra Mary; April 21, 1926, London) - Queen of Great Britain from 1952 to the present.
Elizabeth II descended from the Windsor dynasty. She ascended the throne on February 6, 1952 at the age of 25 after the death of her father, King George VI.
She is the head of the British Commonwealth of Nations and, in addition to Great Britain, the queen of 15 independent states: Australia, Antigua and Barbuda, the Bahamas, Barbados, Belize, Grenada, Canada, New Zealand, Papua New Guinea, St. Vincent and the Grenadines, St. Kitts and Nevis, St. Lucia, Solomon Islands, Tuvalu, Jamaica. He is also the head of the Anglican Church and the supreme commander of the armed forces of Great Britain.
Elizabeth II- the oldest British (English) monarch in history. She is currently the second longest-serving head of state in history (after Queen Victoria) and also the second longest-serving head of state in the world (after King Bhumibol Adulyadej of Thailand). She is also the oldest female head of state in the world.
For the reign Elizabeth a very wide period of British history falls out: the process of decolonization was completed, which was marked by the final collapse of the British Empire and its transformation into the Commonwealth of Nations. This period also included many other events, such as the long ethno-political conflict in Northern Ireland, the Falklands War, the wars in Iraq and Afghanistan.
Throughout her reign, the queen has been criticized more than once not only by British Republicans, but also by various British media, as well as by the general public. Nevertheless, Elizabeth II was able to maintain the prestige of the British monarchy and her popularity in the UK is at its best.
Childhood and youth of Elizabeth II
Eldest daughter of Prince Albert, Duke of York (future King George VI, 1895-1952) and Lady Elizabeth Bowes-Lyon (1900-2002). Her grandparents are: on her father's side - King George V (1865-1936) and Queen Mary, Princess of Teck (1867-1953); by mother - Claude George Bowes-Lyon, Earl of Strathmore (1855-1944) and Cecilia Nina Bowes-Lyon (1883-1961).
Princess Elizabeth Alexandra Mary was born in London's Mayfair at the residence of the Earl of Strathmore at Brewton Street, house number 17. Now the area has been rebuilt, and the house no longer exists, but a memorial plaque has been erected on this site. She got her name in honor of her mother (Elizabeth), grandmother (Maria) and great-grandmother (Alexandra).
At the same time, the father insisted that the first name of the daughter be like that of the duchess. At first they wanted to give the girl the name Victoria, but then they changed their minds. George V remarked: “Bertie discussed the name of the girl with me. He named three names: Elizabeth, Alexandra and Mary. The names are all good, I told him so, but about Victoria, I absolutely agree with him. It was redundant." The christening of Princess Elizabeth took place on May 25 in the chapel of Buckingham Palace, later destroyed during the war years.
In 1930, Elizabeth's only sister, Princess Margaret, was born.
Elizabeth received a good education at home, mainly in the humanities - she studied the history of the constitution, law, religious studies, art history, and also (actually independently) French. From a young age, Elizabeth was interested in horses and was engaged in horseback riding. She has been faithful to this hobby for many decades.
At birth Elizabeth became the Duchess of York and was third in the line of succession to the throne after her uncle Edward, Prince of Wales (future King Edward VIII) and father. Since Prince Edward was young enough to be expected to marry and have children, Elizabeth was not initially considered a viable candidate for the throne. However, Edward was forced to abdicate just a few months after the death of George V in 1936. Prince Albert (George VI) became king, and 10-year-old Elizabeth became heir to the throne and moved with her parents from Kensington to Buckingham Palace. At the same time, she remained in the role of "heir presumptive" ("supposed heir") (English) Russian, and if George VI had a son, he would have inherited the throne.
World War II began when Elizabeth was 13 years old. On October 13, 1940, she made her first radio appearance, addressing children affected by the disasters of the war. In 1943, her first independent appearance in public took place - a visit to the regiment of the Guards Grenadiers. In 1944, she became one of the five "state councilors" (persons entitled to perform the functions of the king in the event of his absence or incapacity). In February 1945, Elizabeth joined the "Auxiliary Territorial Service" - women's self-defense units - and was trained as an ambulance driver, receiving the military rank of lieutenant.
In 1947, Elizabeth accompanied her parents on a trip to South Africa and, on her 21st birthday, went on the radio with a solemn promise to devote her life to the service of the British Empire.
In the same year, 21-year-old Elizabeth married 26-year-old Philip Mountbatten, an officer in the British Navy, a member of the Greek and Danish royal families and great-great-grandson of Queen Victoria. They met in 1934, and fell in love, it is believed, after Elizabeth visited the Naval College in Dartmouth, where Philip studied, in 1939. Having become the spouse of the princess, Philip received the title of Duke of Edinburgh.
A year after the wedding, in 1948, the eldest son, Prince Charles, was born to Elizabeth and Philip. And on August 15, 1950, the daughter is Princess Anna.
Queen Elizabeth II of Great Britain
Coronation and beginning of the reign of Elizabeth II
King George VI, father Elizabeth, died February 6, 1952. Elizabeth, who at that time was on vacation with her husband in Kenya, was proclaimed Queen of Great Britain.
The coronation ceremony of Queen Elizabeth II took place at Westminster Abbey on June 2, 1953. This was the first televised coronation of a British monarch, and is credited with having contributed significantly to the rise of television broadcasting.
After that, in 1953-1954. The queen made a six-month tour of the Commonwealth, British colonies and other countries of the world. Elizabeth II became the first monarch to visit Australia and New Zealand.
Second half of the 1950s - early 1990s
In 1957, after the resignation of Prime Minister Sir Anthony Eden, due to the lack of clear rules for choosing a leader in the Conservative Party, Elizabeth II had to appoint a new head of government from among the Conservatives. After consultations with prominent members of the party and former Prime Minister Churchill, 63-year-old Harold Macmillan was appointed head of government.
In the same year, Elizabeth made her first visits to the United States and Canada as Queen of Canada. In the same year, she spoke for the first time at a session of the UN General Assembly. She was present at the opening session of the Canadian Parliament (for the first time in history with the participation of the British monarch). She continued her travels in 1961 when she made visits to Cyprus, the Vatican, India, Pakistan, Nepal, Iran, and Ghana.
Meeting of Elizabeth II with the heads of the Commonwealth countries in 1960
In 1960, the Queen had a second son, Prince Andrew, and in 1964, a third son, Prince Edward.
In 1963, following the resignation of Prime Minister Macmillan, on his advice, Elizabeth appointed Alexander Douglas-Home as prime minister.
In 1974, a political crisis began to brew after parliamentary elections, in which none of the parties received a majority of votes. Although the Conservative Party turned out to be the largest party in Parliament, Labor leader Harold Wilson was appointed Prime Minister. A year later, a political crisis also occurred in Australia (English) Russian, during which Elizabeth II refused to cancel the decision of the governor general to resign the country's prime minister.
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_NY4CNDGu0w
In 1976 Elizabeth II solemnly opened (as Queen of Canada) the XXI Olympic Games in Montreal.
1977 was an important date for the Queen - the 25th anniversary of Elizabeth II's tenure on the British throne was celebrated, in honor of which many ceremonial enterprises were held in the Commonwealth countries.
In the late 1970s and early 1980s, a number of assassination attempts were made on the royal family. In particular, in 1979, the terrorists of the "Provisional Irish Republican Army" assassinated the uncle of Prince Philip, an influential statesman and military leader, Lord Louis Mountbatten. And in 1981, there was an unsuccessful assassination attempt on Elizabeth II during a military parade in honor of the queen's "official birthday".
In 1981, the wedding of the son of Elizabeth II, Prince Charles and Diana Spencer took place, which would later become a big problem for the royal family.
Elizabeth II walking near Windsor Castle with Ronald Reagan (1982)
At this time in 1982, as a result of changes in the Canadian constitution, the British Parliament lost any role in Canadian affairs, but the British Queen still remained the head of the Canadian state. In the same year, the first visit of Pope John Paul II to Great Britain in the last 450 years took place (the Queen, who is the head of the Anglican Church, received him personally).
In 1991, Elizabeth became the first British monarch to address a joint session of the US Houses of Congress.
Turkish President Abdullah Gul and Queen Elizabeth II. London. 2010
Elizabeth II and the Obamas.
Early 1990s - 2000s in the life of Elizabeth II
1992 was a "terrible year", according to the definition of Elizabeth II herself. Two of the Queen's four children - Prince Andrew and Princess Anne - divorced their spouses, Prince Charles separated from Princess Diana, Windsor Castle was badly damaged by fire, the obligation for the Queen to pay income tax was introduced, and funding for the royal court was noticeably reduced.
In 1994, Elizabeth II visited Russia. This was the first visit of the head of the British royal house to the Russian state in the entire history of bilateral relations dating back to 1553.
In 1996, at the urging of the Queen, a formal divorce was signed between Prince Charles and Princess Diana. A year later, in 1997, the tragic death of Princess Diana in a car accident in Paris occurred, which shocked not only the royal family, but also millions of ordinary Britons. For restraint and the absence of any reaction to the death of the former daughter-in-law, critical remarks immediately rained down on the Queen.
In 2002, solemn events were held in honor of the 50th anniversary of Elizabeth II on the British throne (Golden Jubilee. But in the same year, the Queen's sister, Princess Margaret, and the Queen Mother, Queen Elizabeth, died.
In 2008, for the first time in history, the Anglican Church, led by Elizabeth, held a Maundy Thursday service, in which the reigning monarch traditionally participates, outside of England or Wales - in the Cathedral of St. Patrick's in Armagh in Northern Ireland.
Modernity
In 2010, she spoke for the second time at a meeting of the UN General Assembly. Introducing the Queen, UN Secretary-General Ban Ki-moon called her "the anchor of our era."
In 2011, the first ever state visit by a British monarch to independent Ireland took place. In the same year, the wedding of Prince William (grandson of Elizabeth II) and Catherine Middleton took place.
In 2012, the XXX Olympic Games were held in London, inaugurated by Elizabeth II, and a new law was approved that changes the order of succession, according to which male heirs lose priority over women.
In the same year, the 60th (“diamond”) anniversary of Elizabeth II on the throne was solemnly celebrated in Great Britain and other countries. The culmination of the festive events was the weekend of June 3-4, 2012:
On June 3, a solemn water parade of more than a thousand ships and boats took place on the Thames. It is believed that this is the most grandiose river procession in history;
On June 4, 2012, a concert took place on the square in front of Buckingham Palace with the participation of such stars of British and world music as Paul McCartney, Robbie Williams, Cliff Richard, Elton John, Grace Jones, Stevie Wonder, Annie Lennox, Tom Jones and others. The evening was hosted by Take That lead singer Gary Barlow.
Elizabeth II and Prince Philip (2013)
In 2013, for the first time in 40 years, Elizabeth II refused to go to the summit of the heads of the countries of the British Commonwealth, held in Sri Lanka. Britain at the summit will be represented by Prince Charles, which indicates the gradual transfer of powers of Elizabeth to her son.
In the same year, the 60th anniversary of the coronation of Elizabeth II was celebrated in Great Britain, but on a smaller scale.
Role in political and public life
In accordance with the British tradition of a constitutional monarchy, Elizabeth II performs mainly representative functions, with little or no influence on the government of the country. However, during her reign, she successfully maintains the authority of the British monarchy. Her duties include visiting various countries on diplomatic visits, receiving ambassadors, meeting with high-ranking government officials (especially the Prime Minister), reading annual messages to Parliament, presenting awards, knighting, etc. The Queen also looks through the main British newspapers daily and answers with the help of servants for some letters, which are sent to her in huge quantities (200-300 pieces daily).
Throughout her time on the throne, the Queen maintained correct relations with all prime ministers. At the same time, she always remained true to the tradition of the English kings of modern times - to be above political fights.
Elizabeth II is also actively involved in charity work. She is a trustee of over 600 different public and charitable organizations.
Main article: Royal prerogatives
In addition to duties, Elizabeth II also has certain inalienable rights, like a monarch (royal prerogatives), which, however, are quite formal. For example, she can dissolve the parliament, reject the candidacy of the prime minister (which seems unsuitable to her), etc.
Financial expenses
Certain funds are spent on the maintenance of the queen from the so-called civil list, which is controlled by the government.
So, according to data from Buckingham Palace, in the 2008-2009 financial year, each Briton spent $ 1.14 on the maintenance of the monarchy, which amounted to $ 68.5 million in total.
In 2010-2011, due to the government's new economic program, the Queen was forced to cut her spending to $51.7 million.
But, starting in 2012, Elizabeth's income began to grow again (at an approximate rate of 5% per year).
Such figures cause dissatisfaction among the Republican-minded part of the British population, which considers it necessary to cut them.
Family and Children
On November 20, 1947, Elizabeth married Lieutenant Philip Mountbatten (born June 10, 1921), the son of the Greek Prince Andrew, who received the title of Duke of Edinburgh.
Four children were born in their family:
Name Date of birth Marriage Children Grandchildren
Prince Charles,
Prince of Wales 14 November 1948 Lady Diana Spencer 29 July 1981
(divorced: 28 August 1996) Prince William, Duke of Cambridge Prince George of Cambridge
Prince Henry (Harry) of Wales
Camille Shand April 9, 2005
Princess Anna,
"Princess Royal" August 15, 1950 Mark Phillips November 14, 1973
(divorced: April 28, 1992) Peter Phillips Savannah Phillips
Isla Elizabeth Phillips
Zara Phillips
Timothy Lawrence December 12, 1992
Prince Andrew
Duke of York 19 February 1960 Sarah Ferguson 23 July 1986
(divorced: 30 May 1996) Princess Beatrice of York
Princess Eugenie (Eugenie) of York
Prince Edward
Earl of Wessex 10 March 1964 Sophie Rhys-Jones 19 June 1999 Lady Louise Windsor
James, Viscount Severn
Official titles, awards and coat of arms
The full title of Elizabeth II in Great Britain sounds like "Her Majesty Elizabeth II, by the grace of God of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland and her other kingdoms and territories, the Queen, Head of the Commonwealth, Defender of the Faith."
During the reign of Elizabeth II, in all countries that recognize the British monarch as their head of state, laws were passed according to which in each of these countries the British monarch acts as head of this particular state (English) Russian, regardless of his titles in Great Britain proper or in third countries. Accordingly, in all these countries, the title of the queen sounds the same, with the name of the state replaced. In some countries, the words "defender of the faith" are excluded from the title. For example, in Australia, the title sounds like this: "Her Majesty Elizabeth II, by the grace of God the Queen of Australia and her other kingdoms and territories, Head of the Commonwealth."
On the islands of Guernsey and Jersey, Elizabeth II also bears the title of Duke of Normandy, on the Isle of Man - the title of "Lord of Maine".
States whose head was or is Elizabeth II
Member countries of the Commonwealth are marked on the map (Fiji membership is suspended)
Upon accession to the throne, in 1952, Elizabeth became queen of seven states: Great Britain, Canada, Australia, New Zealand, South Africa, Pakistan and Ceylon.
During her reign, some of these countries became republics. At the same time, as a result of the process of decolonization, numerous British colonies gained independence. In some of them, the Queen of Great Britain retained the status of head of state, in others she did not.
Abolition of the monarchy in the original possessions of Elizabeth II:
Pakistan - in 1956 (former Dominion of Pakistan).
South Africa - in 1961 (former South Africa).
Ceylon (Sri Lanka) - in 1972 (former Dominion of Ceylon).
Blue indicates states that retain the monarchy
Newly independent states that retained the monarchy:
Antigua and Barbuda
Bahamas
Barbados
Belize
Grenada
Papua New Guinea
Saint Vincent and the Grenadines
Saint Kitts and Nevis
Saint Lucia
Solomon islands
Tuvalu
Jamaica
Newly independent states that abandoned the monarchy:
Guyana
Gambia
Ghana
Kenya
Mauritius
Malawi
Malta
Nigeria
Sierra Leone
Tanganyika
Trinidad and Tobago
Uganda
Fiji
Awards
Main article: Titles and honors of Elizabeth II
Elizabeth II in Great Britain and the Commonwealth countries, as well as in other states, is the head of a number of knightly orders, and also has military ranks, numerous honorary titles, academic degrees. In addition, she is a holder of various domestic British awards, as well as a number of various awards from foreign countries.
Coats of arms in different periods of time and in different countries
Coat of arms of Princess Elizabeth (1944-1947)
Coat of arms of Princess Elizabeth, Duchess of Edinburgh (1947-1952)
Royal coat of arms in Great Britain (except Scotland)
Royal coat of arms in Scotland
Royal coat of arms in Canada
public perception
At the moment, the majority of Britons positively assess the activities of Elizabeth II as a monarch (about 69% believe that the country would be worse without the monarchy; 60% believe that the monarchy contributes to raising the country's image abroad and only 22% were against the monarchy).
Criticism
Despite the positive attitude of most of her subjects, the queen was repeatedly criticized throughout her reign, in particular:
In 1963, when a political crisis arose in Britain, Elizabeth was criticized for having personally appointed Alexander Douglas-Home as Prime Minister of Great Britain.
In 1997, for the lack of an immediate reaction to the death of Princess Diana, the queen fell not only with the anger of the British public, but even of many major British media (for example, The Guardian).
In 2004, after Elizabeth II beat a pheasant to death with a cane, a wave of indignation from environmental organizations swept across the country about the actions of the monarch.
Hobbies and personal life
Map of visits by Elizabeth II around the world
The Queen's interests include dog breeding (including Corgis, Spaniels and Labradors), photography, horseback riding, and travel. Elizabeth II, maintaining her prestige of the Queen of the Commonwealth, travels very actively in her possessions, and also visits other countries of the world (for example, in 1994 she visited Russia). She has more than 325 foreign visits to her credit (during her reign, Elizabeth visited more than 130 countries).
I have been gardening since 2009.
In addition to English, he is also fluent in French.
Memory
In culture
Films about Elizabeth II
In 2004, the film Churchill: The Hollywood Years was released - “Churchill Goes to War!”, Where the role of Elizabeth was played by Neve Campbell.
In 2006, the biopic The Queen was released. The role of the queen was played by actress Helen Mirren. The film is a BAFTA winner in the Best Film category. Actress Helen Mirren, who played the title role in the film, won the Oscar, Golden Globe, BAFTA, and the Volpi Cup at the Venice Film Festival for Best Actress. In addition, the film was nominated for an Oscar as Best Picture.
In 2009, the 4th channel of British television (Channel 4) filmed a 5-episode fictional mini-series "The Queen" ("The Queen", directed by Edmund Coulthard, Patrick Reams). The Queen at different periods of her life was played by 5 actresses: Emilia Fox, Samantha Bond, Susan Jameson, Barbara Flynn, Diana Quick.
On July 27, 2012, the television broadcast of the opening ceremony of the Summer Olympic Games in London began with a video featuring James Bond (Daniel Craig) and the Queen (cameo). At the end of the video, they both parachute from a helicopter over the arena of the Olympic Stadium. On April 5, 2013, for this role, the Queen was awarded the BAFTA Award for the best performance of the role of a James Bond girl.
In architecture
In honor of the queen, Elizabeth Avenue is named next to the espalana in Singapore.
The famous Big Ben, the symbol of London, has been officially called the “Elizabeth Tower” since September 2012.
A bridge in Duford, completed in 1991, is also named after the Queen.
On August 1, 2013, the Elizabeth II Olympic Park was opened in London.
Lifetime monuments
Lifetime monuments
Statue of Elizabeth II in Ottawa, Parliament Hill, Canada
Statue in Regina, Saskatchewan, erected in 2005
Statue in Windsor Great Park
In botany
In honor of Elizabeth II, the rose variety Rosa "Queen Elizabeth" was named.
On coins and in philately
Coins and postage stamps
On a Canadian stamp, 1953
On an Australian coronation stamp
On a Northern Ireland stamp, 1958
On a 1953 coin
On a South African coin, 1958
Coin with Elizabeth 1961
In geography
The name of Elizabeth II was repeatedly assigned to various territories, among them:
Princess Elizabeth Land in Antarctica
Queen Elizabeth Land in Antarctica
Queen Elizabeth Islands in Canada
Elizabeth fell in love with Philip at first sight: they met when she was 13 years old and he was 18. A well-built blond, a cadet of the Royal Naval College, right away. Correspondence began between her and Philip.
2. Elizabeth's parents were against her marriage to Philip
Philip comes from a royal family: at birth, he bore the title of Prince of Greece and Denmark. However, Philip's family was expelled from Greece. Leaving his native country, his relatives settled in Paris, and Philip was sent to London, where he studied, received the rank of midshipman and went to serve in the navy during World War II. Although the young man wrote long and tender letters to the future Queen of England from the front, Elizabeth's relatives were not at all delighted with the choice of their daughter. They believed that Philip was not a couple for the princess - his family was ruined. The only inheritance that Philip received from his father was a signet ring.
3. Philip had to give up his title and religion
The wedding of Philip and Elizabeth, however, still took place. True, for her sake the young man had to sacrifice a lot. So, he ceased to be called a Greek prince, became a British subject and switched from Orthodoxy to Anglicanism. He was ready to forever remain in history as the queen's husband.
4. The wedding of Elizabeth and Philip was modest
Elizabeth and Philip got married at the end of 1947 - then the war had just ended ... The wedding was played by royal standards, rather modest, although very beautiful. The dress for the main day in her life was sewn by court fashion designer Norman Hartnell, who was inspired by Sandro Botticelli's painting "Spring". “I discovered a painting by Botticelli in the museum, which depicted a girl in ivory silk flowing along her body, strewn with jasmine flowers, asparagus and rosebuds. I recreated all this flora with the help of crystal beads and pearls,” he recalled. Elizabeth's head was adorned with her mother's precious tiara, and two pages carried a five-meter veil. The outfit was complemented by satin heeled sandals, the silver buckles of which were decorated with pearls.
5. Philip became the first to take the oath of allegiance to Elizabeth as queen.
Elizabeth and Philip after the wedding were inseparable. The girl took care of the house and was happy as a wife. Soon the couple had children - Charles and Anna. But in February 1952, the measured life of the family ended. The King of England and Elizabeth's father, George VI, died of a blood clot in his heart ... Philip was the first who, on bended knee, took an oath of allegiance to Elizabeth II as queen.
6. At first, Elizabeth forbade Philip from giving his children his last name.
After the coronation of Elizabeth, Philip had not only to leave the service in the navy, but to devote himself entirely to royal duties. He accompanied the queen on all trips, helped her in public affairs ... The man dreamed that his wife and children would bear his last name, but then the Windsors would officially cease to be rulers - and Mountbatten would become. The mere thought of this aroused indignation among all of Elizabeth's relatives. The Queen consulted with Prime Minister Winston Churchill and refused her husband's request to assign his surname to Charles and Anne. Philip was very worried and joked bitterly, calling himself the only person in the country who could not give his family name to his own children.
7. Philip and Elizabeth were on the verge of a divorce
In the mid-50s, Elizabeth was all absorbed in state affairs, and Philip suffered because he had to leave the service in the navy. The relationship of the spouses became cool and, perhaps, things even went to divorce - but the duke unexpectedly found himself in charity work. And then Elizabeth became pregnant again - and suddenly allowed her husband to give the newborn boy Andrew her last name. The fourth child of the royal couple, Edward, also received his father's surname. Thus, the couple's older children, Charles and Anna, have the surname Windsor, while the younger ones, Andrew and Edward, have Mountbatten-Windsor.
Her Majesty Queen Elizabeth II, Elizabeth Alexandra Mary Windsor (Queen Elizabeth II, Elizabeth Alexandra Mary Windsor; b. April 21, 1926, London) is the 12th queen and head of state of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, is also the queen of 15 states of the Commonwealth of Nations (Australia, Antigua and Barbuda, Bahamas, Barbados, Belize, Grenada, Canada, New Zealand, Papua New Guinea, Saint Vincent and the Grenadines, Saint Kitts and Nevis, Saint Lucia, Solomon Islands, Tuvalu, Jamaica), chapter Church of England, Supreme Commander of the Armed Forces and Lord of the Isle of Man. She was also Queen of South Africa from 29 May 1953 to 31 May 1961.
Eldest daughter of the Duke of York George, the future King of Great Britain George VI (1895-1952)
and Lady Elizabeth Bowes-Lyon (1900–2002).
Her grandparents: George V (1865-1936), King of Great Britain
and Queen Mary (1867-1953), Princess of Teck, - by father,
Claude George Bowes-Lyon (1855–1944), Earl of Strathmore and Cecilia Nina Bowes-Lyon (1883–1961), by mother.
Early years of Elizabeth II
1. The Queen was born at 2:40 am on April 21, 1926 in London's Mayfair at the residence of the Earl of Strathmore on Brewton Street, house number 17.
2. She was the first child of the Duke and Duchess of York, who would go on to become King George VI and Queen Elizabeth.
3. At the time, she was third in the line of succession to the throne after Edward, Prince of Wales (later King Edward VIII) and her father, the Duke of York. But no one expected her father to become a king, much less that she would become a queen.
4. Princess Elizabeth was baptized with the names of Alexander and Mary in the chapel of Buckingham Palace. She was named after her mother, and her two middle names are after her paternal great-grandmother, Queen Alexandra, and her paternal grandmother, Queen Mary.
5. The Princess's early years were spent at 145 Piccadilly, her parents' London home, where they moved shortly after her birth, and at the White House in Richmond Park.
6. When she was six years old, her parents received government positions at the Royal House in Windsor Great Park.
7. Princess Elizabeth was educated at home with Princess Margaret, her younger sister.
8. Elizabeth was personally educated by her father, King George, and also had classes with Henry Marten, vice-rector of Eton. The Archbishop of Canterbury studied religion with her.
9. Princess Elizabeth learned French from French and Belgian governesses. This skill served the Queen well, as she was personally able to take part in conversations with ambassadors and heads of state from French-speaking countries, as well as when visiting French-speaking areas of Canada.
Princess Elizabeth in 1933
10. Princess Elizabeth became a Scout when she was eleven years old and then became a Marine Ranger.
11. In 1940, at the height of the war, the young princesses were moved for their safety to Windsor Castle, where they spent most of the war years.
1943 with sister
Women's Auxiliary Territorial Corps: Princess Elizabeth, 2nd Chief of the Department of Internal Affairs, in overalls.
royal romance
12. The Queen is the first British monarch to celebrate a Diamond Jubilee.
13. Princess Elizabeth and Prince Philip met at the wedding of Prince Philip's cousin, Princess Marina of Greece and the Duke of Kent, who was Princess Elizabeth's uncle, in 1934.
14. The engagement of Princess Elizabeth and Lieutenant Philip Mountbatten was announced on July 9, 1947. Prince Philip at birth received the title of Prince of Greece and Denmark. He joined the Navy in 1939 and after the war, in February 1947, he became a British citizen. Prince Philip had to choose a surname in order to continue his career in the Royal Navy and he adopted the surname of his mother's British relatives, Mountbatten. At the wedding, King George VI elevated him to the title of Duke of Edinburgh.
15. Royal wedding rings were decorated with platinum and encrusted with diamonds by jeweler Philip Antrobus. He used diamonds from a diadem belonging to the mother of Prince Philip in jewelry.
16. Prince Philip had two bachelor parties before the wedding: the first - official in Dorchester, which included invited guests from the press, and the second - with close friends at the Belfrey club.
17. The Queen and the Duke of Edinburgh were married at Westminster Abbey on 20 November 1947 at 11:30 am. The celebration was attended by 2000 invited guests.
Video: "Wedding"
Bridesmaid dresses were made in the same style. They were made from cheaper materials (also purchased with coupons), but due to the embroidery and interesting design, they looked decent.
Princess Margaret as a bridesmaid at Queen Elizabeth's wedding
Princess Alexandra of Kent as a bridesmaid at the Queen's wedding
18. Elizabeth had eight bridesmaids: Her Royal Highness Princess Margaret, Princess Alexandra of Kent, Lady Caroline Montagu-Douglas-Scott, Lady Mary Cambridge, Lady Elizabeth Lambert, Pamela Mountbatten, Margaret Elphinstone, Diana Bowes-Lyon.
19. Also in attendance at the wedding were HRH Prince William of Gloucester (aged five) and HRH Prince Michael of Kent (also aged five).
20. The Queen's wedding dress was designed by Sir Norman Hartnell.
21. The fabric for the dress was specially made by "Winterthur Silks Limited" in Dunfermline, at the Canmore factory. For its manufacture, threads of Chinese silkworms were delivered from China. Garlands of flowers of orange fleur (the emblem of virginity), jasmine (the emblem of happiness, purity, sincerity) and the white rose of York (white rose means purity) were embroidered with small pearls and crystal rhinestones located all over the dress.
22. The queen's veil was made of light sheer fabric and topped with a diamond tiara. This tiara (which can be worn as a necklace) was made for Queen Mary in 1919. The diamonds from which it is made are taken from a necklace and tiara purchased by Queen Victoria from Collingwood and a wedding gift for Queen Mary in 1893. In August 1936, Queen Mary gave the tiara to Queen Elizabeth when she was still Princess Elizabeth for a future wedding.
Elizabeth "borrowed" the tiara from her mother. An hour before the celebration in the hands of the bride, the tiara broke in half and had to wait for the jeweler, who urgently repaired it.
23. The Tomb of the Unknown Soldier in the Abbey is the only stone that is not covered with a special cover. The day after the wedding, Princess Elizabeth, following the royal tradition begun by her mother, sent the bridal bouquet back to the abbey, where flowers were laid on the grave.
24. The bride's engagement ring was made from a Welsh gold nugget shipped from the Clogau St David mine near Dolgello.
25. About 10 thousand congratulatory telegrams were received at Buckingham Palace, and the royal couple received more than 2,500 wedding gifts from well-wishers around the world.
26. In addition to jewelry, the couple received many useful items for the kitchen and home from close relatives, including salt shakers from the Queen Mother, a bookcase from Queen Mary, and a picnic set from Princess Margaret.
27. "Wedding breakfast" (lunch) was held after the wedding ceremony in Westminster Abbey in the Round Dining Room at Buckingham Palace. The menu included filet de Sole Mountbatten, Pedro casserole, Princess Elizabeth ice cream.
28. On their honeymoon, the couple left Waterloo Station with the princess's dog, Susan.
29. The newlyweds spent their wedding night in Hampshire, at the home of Prince Philip's uncle Earl Mountbatten. The second part of the honeymoon took place in Birkhall, on the Balmoral estate.
30. In early 1948, the couple rented their first family home, Windlensham Moor, in Surrey, near Windsor Castle, where they remained until they moved into Clarence House on July 4, 1949.
31. After marrying Princess Elizabeth, the Duke of Edinburgh continued his naval career, rising to the rank of lieutenant commander in command of the frigate HMS Magpie.
32. Although he was the husband of the Queen, the Duke of Edinburgh was not crowned or anointed at the coronation ceremony in 1953. He was the first to pay respect and take the oath to Her Majesty. He kissed the newly crowned Queen with the words: "I, Philip, Duke of Edinburgh, will be your vassal in sickness and in health, I will serve you faithfully, with honor and respect, until death. May God help me."
Herbert James Gunn Coronation Portrait of Queen Elizabeth II
33. Prince Philip accompanied the Queen on all her travels to Commonwealth countries and state visits, as well as to state events and meetings in all parts of the UK. The first of these was the Commonwealth Coronation Tour from November 1953 to May 1954, in which the couple visited Bermuda, Jamaica, Panama, Fiji, Tonga, New Zealand, Australia, the Cocos Islands, Ceylon, Aden, Uganda, Libya, Malta and Gibraltar, having traveled a distance of 43.618 kilometers.
34. The coronation took place at Westinster Abbey on June 2, 1953. The ceremony was officiated by Geoffrey Fisher, Archbishop of Canterbury.
35. The coronation was broadcast in every part of London, on the navy, in Scotland, Northern Ireland and Wales.
Sketch by Norman Hartnell for the coronation dress of Elizabeth II
Coronation dress by Norman Hartnell
Joan Hassell. Prince Charles invitation, 1953
36. The Queen and Duke Philip of Edinburgh have four children: Prince Charles, Prince of Wales (b. 1948), Princess Anne (b. 1950), Prince Andrew, Duke of York (b. 1960) and Prince Edward, Earl of Wessex (b. 1964).
37. With the birth of Prince Andrew in 1960, the Queen became the first reigning monarch to have a child since Queen Victoria, whose youngest child, Princess Beatrice, was born in 1857.
Prince Charles, Prince of Wales (b. 1948)
Princess Anne, (b. 1950)
The Queen with son Charles and daughter Anne, 1954
The Queen, the Duke of Edinburgh, the Duke of Cornwall and Princess Anne October 1957
Prince Andrew, Duke of York (b. 1960)
Queen Elizabeth II's two youngest children, Princes Andrew and Edward.
Prince Edward, Earl of Wessex (b. 1964)
Prince Edward and Princess Sophie
38. The Queen and Duke of Edinburgh Philip have eight grandchildren -
Peter Phillips (b. 1977)
Zara Phillips (b. 1981)
Prince William (b. 1982)
Prince Harry (b. 1984),
Princess Beatrice (b. 1988),
Princess Eugenie (b. 1990),
Lady Louise Windsor (b. 2003)
and James, Viscount Severns (b. 2007),
has a great-granddaughter - Savannah (born in 2011) and great-grandson Prince George of Cambridge (2013)
The Queen and Prince Philip pose with their grandchildren (l-r) William, Harry, Zara and her brother Peter (back row) in a warm portrait sent out for Christmas 1987
Speeches of the Queen of England
39. The Queen televises a Christmas message every year except in 1969, when she decided the royals had had enough on television after an unprecedented documentary about her family. Her greeting took the form of a written address.
40. In a 1991 message, the Queen dismissed rumors of an abdication, as she pledged to continue her service.
41. The Queen issued an injunction against The Sun in 1992 after it published the full text of her speech two days before it was broadcast. She later accepted an apology and a £200,000 donation to charity.
42. The Queen's grandfather, King George V, was the first of the royal family to speak live on the radio from Sandringham on Christmas Day in 1932.
43. George V was at first against the use of wireless devices for transmitting information, but eventually agreed.
44. There was no Christmas broadcast in 1936 and 1938.
45. In 2010, the Queen's speech was broadcast from Hampton Court Palace - the first time a historic building was used.
46. Each speech is written personally by the Queen, each has a strict religious framework, reflects current issues and is often based on her own experience.
Interests and hobbies
48. An animal lover since childhood, the Queen has a keen and very knowledgeable interest in horses. As an owner and breeder of Thoroughbreds, she often comes to watch races to see how her horses are doing on the run, and often attends equestrian events.
49. Elizabeth II took part in the derby, one of the classic races in the UK, and the summer race at Ascot, which has become royal since 1911.
50. The Queen's horses have won several races at Royal Ascot. Notable was the double victory on June 18, 1954, when Landau won the Rous Memorial Stakes and a stallion named Halo won the Hardwicke Stakes, and in 1957 the Queen had four winners during the race.
Zara Philips, Princess Ahn and Elizabeth II
In her young grandchildren (children of Prince Edward), Elizabeth II also encourages horses.
51. Other interests include walks in nature and in the countryside. The Queen also loves to walk with her Labradors, which were specially bred in Sandgreenham.
52. Less well known is the Queen's interest in Scottish dance. Each year during her stay at Balmoral Castle, the Queen hosts a dance known as the "Gillis Ball" for neighbors, estate owners, castle employees and members of the local community.
53. The Queen is the only person in the UK who can drive without a license or registration number in her car. And she doesn't have a passport.
54. The Queen is the patron of over 600 charities.
55. To formally greet the queen, men should bow their heads slightly, while women make a small curtsy. When introduced to the Queen, the proper formal address is "Your Majesty" followed by "Ma'am".
Leisure Queen
56. Queen Elizabeth II is the fortieth English monarch since William the Conqueror.
57. She has traveled to Australia 15 times, Canada 23 times, Jamaica 6 times and New Zealand 10 times.
58. Her Majesty sent about 100,000 telegrams to centenarians in the UK and Commonwealth countries.
59. The Queen dined on 23 ships and interacted with five astronauts at Buckingham Palace.
60. She made her first airplane flight in July 1945.
61. Her Majesty is the only British monarch in history who knows how to change spark plugs.
62. On VE Day, the Queen and her sister Princess Margaret slipped in the crowd during the celebration.
63. For a wedding dress, the Queen collected coupons for clothes.
64. The Queen has a bank account at Coutts & Co.
65. The Queen celebrated her golden jubilee in 2002 by visiting 70 cities and towns across the UK.
66. Tony Blair was the first prime minister to be born during her reign, which has already seen nine prime ministers before him.
67. The Queen attended 91 state banquets and posed for 139 official portraits.
68. Formally, the Queen of England still owns sturgeons, whales and dolphins in the water throughout the UK, which are recognized as "King's Fish". In addition, she owns all wild flocks of swans living in open water.
69. The Queen developed a new breed of dog known as "dorgi" when one of the corgis was bred to a dachshund named Pipkin.
70. The Queen is the first British monarch to see three child divorces.
71. Her Majesty demoted a footman for serving whiskey to her corgi.
72. The Queen has nine Royal Thrones: one in the House of Lords, two in Westminster Abbey and six in the throne room at Buckingham Palace.
73. She is a patron of the Royal Pigeon Racing Association. One of the queen's birds is called the Sandringham Lightning.
74. There have been six Archbishops of Canterbury during the Queen's reign.
75. The height of the Queen is 5 feet 4 inches or 160 centimeters.
Elizabeth II (Elizabeth II), full name - Elizabeth Alexandra Mary (Elizabeth Alexandra Mary). Born April 21, 1926 in London. Queen of Great Britain since 1952.
She ascended the throne on February 6, 1952 at the age of twenty-five, after the death of her father, King George VI. Is among all the monarchs in the history of Great Britain.
The oldest British (English) monarch in history.
She also ranks second in the world in terms of tenure as head of state among all current heads of state (after King Bhumibol Adulyadej of Thailand). She is the world's oldest female current head of state, and in Europe the oldest current head of state.
He is the oldest reigning monarch in the world since January 24, 2015, after the death of King Abdullah ibn Abdulaziz Al Saud of Saudi Arabia.
Comes from the Windsor dynasty.
She is the head of the British Commonwealth of Nations and, in addition to Great Britain, the queen of fifteen independent states: Australia, Antigua and Barbuda, the Bahamas, Barbados, Belize, Grenada, Canada, New Zealand, Papua New Guinea, St. Vincent and the Grenadines, St. Kitts and Nevis, St. Lucia, Solomon Islands, Tuvalu, Jamaica.
He is also head of the Anglican Church and Supreme Commander of the British Armed Forces.
Queen of Great Britain
Eldest daughter of Prince Albert, Duke of York (future King George VI, 1895-1952) and Lady Elizabeth Bowes-Lyon (1900-2002). Her grandparents are: on her father's side - King George V (1865-1936) and Queen Mary, Princess of Teck (1867-1953); by mother - Claude George Bowes-Lyon, Earl of Strathmore (1855-1944) and Cecilia Nina Bowes-Lyon (1862-1938).
Princess Elizabeth Alexandra Mary was born in London's Mayfair at the residence of the Earl of Strathmore at Brewton Street, house number 17. Now the area has been rebuilt, and the house no longer exists, but a memorial plaque has been erected on this site. She got her name in honor of her mother (Elizabeth), grandmother (Maria) and great-grandmother (Alexandra).
At the same time, the father insisted that the first name of the daughter be like that of the duchess. At first they wanted to give the girl the name Victoria, but then they changed their minds. George V remarked: “Bertie discussed the girl's name with me. He named three names: Elizabeth, Alexandra and Mary. The names are all good, I told him so, but about Victoria, I absolutely agree with him. It was redundant".

The christening of Princess Elizabeth took place on May 25 in the chapel of Buckingham Palace, later destroyed during the war years.
In 1930, Elizabeth's only sister, Princess Margaret, was born.
She received a good education at home, mainly in the humanities - she studied the history of the constitution, jurisprudence, religious studies, art history, and also (actually independently) French.
From a young age she was interested in horses and was engaged in horseback riding. She has been faithful to this hobby for many decades.
At birth, Elizabeth became the Princess of York and was third in the line of succession to the throne after her uncle Edward, Prince of Wales (future King Edward VIII) and father. Since Prince Edward was young enough to be expected to marry and have children, Elizabeth was not initially considered a viable candidate for the throne.
However, Edward was forced to abdicate eleven months after the death of George V in 1936. Prince Albert (George VI) became king, and 10-year-old Elizabeth became heir to the throne and moved with her parents from Kensington to Buckingham Palace. However, she remained in the role "heir presumptive"("presumptive heir"), and if George VI had a son, he would have inherited the throne.
World War II began when Elizabeth was 13 years old.
On October 13, 1940, she made her first radio appearance, addressing children affected by the disasters of the war.
In 1943, her first independent appearance in public took place - a visit to the regiment of the Guards Grenadiers.
In 1944, she became one of the five "state councilors" (persons entitled to perform the functions of the king in the event of his absence or incapacity).
In February 1945, Elizabeth joined the "Auxiliary Territorial Service" - women's self-defense units - and was trained as an ambulance driver, receiving the military rank of lieutenant. Her military service lasted five months, which gives reason to consider her the last participant in World War II who has not yet retired (the penultimate one was Pope Benedict XVI, who served as an anti-aircraft gunner in the German armed forces).

In 1947, Elizabeth accompanied her parents on a trip to South Africa and, on her 21st birthday, went on the radio with a solemn promise to devote her life to the service of the British Empire.
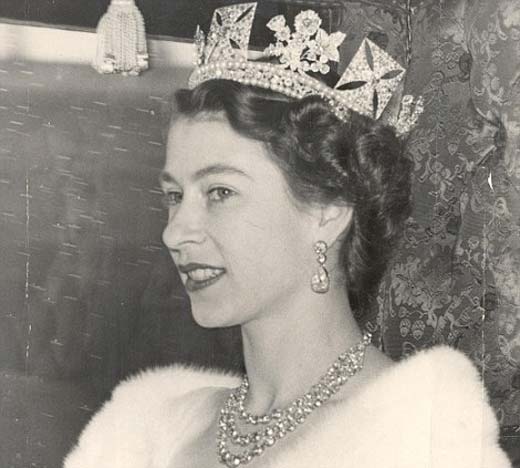

King George VI, Elizabeth's father, died February 6, 1952. Elizabeth, who at that time was on vacation with her husband in Kenya, was proclaimed Queen of Great Britain.
The coronation ceremony of Queen Elizabeth II took place at Westminster Abbey on June 2, 1953. This was the first televised coronation of a British monarch, and is credited with having contributed significantly to the rise of television broadcasting.
Coronation of Elizabeth II
The full title of Elizabeth II in Great Britain sounds like "Her Majesty Elizabeth II, by the grace of God of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland and her other kingdoms and territories, the Queen, Head of the Commonwealth, Defender of the Faith".

After that, in 1953-1954. The queen made a six-month tour of the Commonwealth, British colonies and other countries of the world.
Elizabeth II became the first monarch to visit Australia and New Zealand.
In 1957, after the resignation of Prime Minister Sir Anthony Eden, due to the lack of clear rules for choosing a leader in the Conservative Party, Elizabeth II had to appoint a new head of government from among the Conservatives. After consultations with prominent members of the party and former Prime Minister Churchill, 63-year-old Harold Macmillan was appointed head of government.
In the same year, Elizabeth made her first visits to the United States and Canada as Queen of Canada. She also spoke for the first time at a session of the UN General Assembly. She was present at the opening session of the Canadian Parliament (for the first time in history with the participation of the British monarch). She continued her travels in 1961 when she made visits to Cyprus, the Vatican, India, Pakistan, Nepal, Iran, and Ghana.
In 1963, following the resignation of Prime Minister Macmillan, on his advice, Elizabeth appointed Alexander Douglas-Home as prime minister.
In 1976, Elizabeth II inaugurated (as Queen of Canada) the XXI Olympic Games in Montreal.
1977 was an important date for the Queen - the 25th anniversary of Elizabeth II's tenure on the British throne was celebrated, in honor of which many ceremonial enterprises were held in the Commonwealth countries.
Late 1970s - early 1980s There have been a number of assassination attempts on the royal family.. In particular, in 1979, the terrorists of the "Provisional Irish Republican Army" assassinated the uncle of Prince Philip (the queen's husband), an influential statesman and military leader, Lord Louis Mountbatten. And in 1981, there was an unsuccessful assassination attempt on Elizabeth II herself during a military parade in honor of the queen's "official birthday".
In 1981, the wedding of the son of Elizabeth II, Prince Charles and, which would later become a big problem for the royal family, took place.

At this time in 1982, as a result of changes in the Canadian constitution, the British Parliament lost any role in Canadian affairs, but the British Queen still remained the head of the Canadian state. In the same year, the first visit of Pope John Paul II to Great Britain in the last 450 years took place (the Queen, who is the head of the Anglican Church, received him personally).
In 1991, Elizabeth became the first British monarch to address a joint session of the US Houses of Congress.
1992 was a "terrible year", according to the definition of Elizabeth II herself. Two of the Queen's four children - Prince Andrew and Princess Anne - divorced their spouses, Prince Charles separated from Princess Diana, Windsor Castle was badly damaged by fire, the obligation for the Queen to pay income tax was introduced, and funding for the royal court was noticeably reduced.
In 1996, at the urging of the Queen, a formal divorce was signed between Prince Charles and Princess Diana.
A year later, in 1997, the tragic death of Princess Diana in a car accident in Paris occurred, which shocked not only the royal family, but also millions of ordinary Britons. For restraint and the absence of any reaction to the death of the former daughter-in-law, critical remarks immediately rained down on the Queen.
In 2002, celebrations were held in honor of the 50th anniversary of Elizabeth II on the British throne (Golden Jubilee). But in the same year, the Queen's sister, Princess Margaret, and the Queen Mother, Queen Elizabeth, died.
In 2008, for the first time in history, the Anglican Church, led by Elizabeth, held a Maundy Thursday service, in which the reigning monarch traditionally participates, outside of England or Wales - in the Cathedral of St. Patrick's in Armagh in Northern Ireland.
In 2010, she spoke for the second time at a meeting of the UN General Assembly. Introducing the Queen, UN Secretary-General Ban Ki-moon called her "the saving anchor of our era."
In 2011, the first ever state visit by a British monarch to independent Ireland took place. In the same year, the wedding of Prince William (grandson of Elizabeth II) and Catherine Middleton took place.

In 2012, the XXX Olympic Games were held in London, inaugurated by Elizabeth II, and a new law was approved that changes the order of succession, according to which male heirs lose priority over women.
In 2012, the UK and other countries solemnly celebrated the 60th (diamond) anniversary of Elizabeth II on the throne. On June 3, a solemn water parade of more than a thousand ships and boats took place on the Thames. It is believed that this is the most grandiose river procession in history. On June 4, 2012, a concert took place on the square in front of Buckingham Palace with the participation of such stars of British and world music as Paul McCartney, Robbie Williams, Cliff Richard, Elton John, Grace Jones, Stevie Wonder, Annie Lennox, Tom Jones and others. The evening was hosted by Take That lead singer Gary Barlow.
In 2013, for the first time in 40 years, Elizabeth II refused to go to the summit of the heads of the countries of the British Commonwealth, held in Sri Lanka. Britain was represented at the summit by Prince Charles, which indicates the gradual transfer of powers of Elizabeth to her son.
The Queen's interests include dog breeding (including Corgis, Spaniels and Labradors), photography, horseback riding, and travel. Elizabeth II, maintaining her prestige of the Queen of the Commonwealth, travels very actively in her possessions, and also happens in other countries of the world: she has more than 325 foreign visits to her account.
I have been gardening since 2009.
In addition to English, he is also fluent in French.
Height of Elizabeth II: 163 centimeters
Personal life of Elizabeth II:
In 1947, at the age of 21, she married 26-year-old Philip Mountbatten (born June 10, 1921) - an officer in the British Navy, a member of the Greek (son of the Greek Prince Andrew) and Danish royal families and great-great-grandson of Queen Victoria.
They met in 1934, and fell in love, it is believed, after a visit by Elizabeth in 1939 to the Naval College in Dartmouth, where Philip studied.
Having become the spouse of the princess, Philip received the title of Duke of Edinburgh.
A year after the wedding - in 1948 - the eldest son was born to Elizabeth and Philip. And on August 15, 1950 - a daughter, Princess Anna.
Elizabeth II and Philip Mountbatten






In 1960, the Queen's second son, Prince Andrew, was born. In 1964, she gave birth to her third son, Prince Edward.
Children of Elizabeth II:
Born November 14, 1948. July 29, 1981 married Lady Diana Spencer. On August 28, 1996, the couple filed for divorce. They had two sons: the Duke of Cambridge and Wales.
Prince William, married to, has two children: Prince George of Cambridge and Princess Charlotte of Cambridge.
Princess Anna, "Princess of royal blood" ("Princess Royal") - was born on August 15, 1950. She was married to Mark Phillips from November 14, 1973 to April 28, 1992 (divorced). The couple had two children: Peter Phillips and Zara Phillips.
Prince Andrew, Duke of York- was born on February 19, 1960. He was married to Sarah Ferguson from July 23, 1986 - May 30, 1996 (divorced). The couple had two daughters: Princess Beatrice of York and Princess Eugenie (Eugenie) of York.
Prince Edward, Earl of Wessex- was born on March 10, 1964. He is married to Sophie Rhys-Jones (the wedding took place on June 19, 1999). The couple have two children: Lady Louise Windsor and James, Viscount Severn.
The role of Elizabeth II in the political and public life of Great Britain:
In accordance with the British tradition of a parliamentary monarchy, Elizabeth II performs mainly representative functions, with little or no influence on the government of the country. However, during her reign, she successfully maintains the authority of the British monarchy. Her duties include visiting various countries on diplomatic visits, receiving ambassadors, meeting with high-ranking government officials (especially the Prime Minister), reading annual messages to Parliament, presenting awards, knighting, etc.
Also, the queen daily looks through the main British newspapers and, with the help of servants, answers some letters that are sent to her in huge quantities (200-300 pieces daily).
Throughout her time on the throne, the Queen maintained correct relations with all prime ministers. At the same time, she always remained true to the tradition of the English kings of modern times - to be above political fights. As a constitutional monarch, Elizabeth II should not publicly express her political likes or dislikes. She has always followed this rule by acting in a non-public manner - so her political views remain unknown.
Three times during her reign, the queen had constitutional problems with the formation of the British government.
In 1957 and 1963, with no clear mechanism for electing a leader in the Conservative Party, it was up to the Queen to decide whom to entrust with the formation of a government after the resignations of Anthony Eden and Harold Macmillan.
In 1957, Anthony Eden refused to advise the Queen on whom to appoint as his successor, and she turned for advice to, as the only conservative prime minister alive at the time (following the precedent for which, after the resignation of Andrew Bonar Law in 1923, King George V consulted Lord Salisbury's father and former Prime Minister Arthur Balfour).
In 1963, Harold Macmillan himself advised Alec Douglas-Home to be his successor. And in 1974, after the resignation of Edward Heath as a result of an unclear election outcome, Elizabeth II appointed opposition leader Harold Wilson as prime minister.
In all these cases, the Queen has acted according to the British constitutional tradition, according to which she should not take any important decisions without the advice of her ministers and privy councillors.
In addition, British prime ministers meet with the Queen every week. The Queen is more knowledgeable on most matters than meets the eye. In addition, the Queen has regular meetings with other Commonwealth ministers and premiers when they are in the UK on a visit. Also, during her stay in Scotland, she meets with the First Minister of Scotland. The British Ministry and diplomatic missions send her regular reports.
Although it is customary that the Queen does not interfere in politics, but due to the fact that during her long reign she had the opportunity to work with many prime ministers and leaders of other countries, her advice is always taken seriously. In her memoirs, she wrote of her weekly meetings with Queen Elizabeth: "Anyone who thinks that they [meetings] are a mere formality or social convention are deeply mistaken. In fact, they take place in a calm business atmosphere, and Her Majesty always demonstrates her ability to cover a wide range of problems and her great experience".
Elizabeth II is actively involved in charity and social activities. The Queen of Britain is a trustee of more than 600 different public and charitable organizations.
In addition to duties, Elizabeth II also has certain inalienable rights as a monarch (royal prerogatives). For example, she can dissolve the parliament, reject the candidacy of the prime minister (which seems unsuitable to her), and so on.
Financial costs for the queen:
So, according to data from Buckingham Palace, in the 2008-2009 financial year, each Briton spent $ 1.14 on the maintenance of the monarchy, which amounted to $ 68.5 million in total.
In 2010-2011, due to the government's new economic program, the Queen was forced to cut her spending to $51.7 million.
Starting in 2012, Elizabeth's income began to grow again (at an approximate rate of 5% per year).
Such figures cause dissatisfaction among the Republican-minded part of the British population, which considers it necessary to cut them.
States whose head was or is Elizabeth II:
Upon accession to the throne in 1952, Elizabeth became queen of seven states: Great Britain, Canada, Australia, New Zealand, South Africa, Pakistan and Ceylon.
During her reign, some of these countries became republics. At the same time, as a result of the process of decolonization, numerous British colonies gained independence. In some of them, the Queen of Great Britain retained the status of head of state, in others she did not.
Abolition of the monarchy in the original possessions of Elizabeth II:
Pakistan - in 1956 (former Dominion of Pakistan)
South Africa - in 1961 (former SA)
Ceylon (Sri Lanka) - in 1972 (former Dominion of Ceylon).
Newly independent states that retained the monarchy:
Antigua and Barbuda
Bahamas
Barbados
Belize
Grenada
Papua New Guinea
Saint Vincent and the Grenadines
Saint Kitts and Nevis
Saint Lucia
Solomon islands
Tuvalu
Jamaica
Newly independent states that abandoned the monarchy:
Guyana
Gambia
Ghana
Kenya
Mauritius
Malawi
Malta
Nigeria
Sierra Leone
Tanganyika
Trinidad and Tobago
Uganda
Fiji
Elizabeth II (eng. Elizabeth II), full name - Elizabeth Alexandra Mary (eng. Elizabeth Alexandra Mary; April 21, 1926, London, UK) - Queen of Great Britain from 1952 to the present. She ascended the throne on February 6, 1952 at the age of twenty-five, after the death of her father, King George VI. He is the longest reigning monarch in British history.
Elizabeth II comes from the Windsor dynasty.
She is the head of the British Commonwealth of Nations and, in addition to Great Britain, the queen of fifteen independent states: Australia, Antigua and Barbuda, the Bahamas, Barbados, Belize, Grenada, Canada, New Zealand, Papua New Guinea, Saint Vincent and the Grenadines, Saint Kitts and Nevis, St. Lucia, Solomon Islands, Tuvalu, Jamaica. He is also head of the Anglican Church and Supreme Commander of the British Armed Forces.
Eldest daughter of Prince Albert, Duke of York (future King George VI, 1895-1952) and Lady Elizabeth Bowes-Lyon (1900-2002). Her paternal grandparents were King George V (1865-1936) and Queen Mary, Princess of Teck (1867-1953); by mother - Claude George Bowes-Lyon, Earl of Strathmore (1855-1944) and Cecilia Nina Bowes-Lyon (1883-1938).
Princess Elizabeth Alexandra Mary was born in London's Mayfair at the residence of the Earl of Strathmore at Brewton Street, house number 17. Now the area has been rebuilt, and the house no longer exists, but a memorial plaque has been erected on this site. She got her name in honor of her mother (Elizabeth), grandmother (Maria) and great-grandmother (Alexandra).
At the same time, the father insisted that the first name of the daughter be like that of the duchess. At first they wanted to give the girl the name Victoria, but then they changed their minds. George V remarked: “Bertie discussed the name of the girl with me. He named three names: Elizabeth, Alexandra and Mary. The names are all good, I told him so, but about Victoria, I absolutely agree with him. It was redundant." The christening of Princess Elizabeth took place on May 25 in the chapel of Buckingham Palace, later destroyed during the war years.
is the current ruling royal family in Great Britain.
The House of Windsor was established on July 17, 1917 by King George V in order to rid the ruling dynasty of the former German name of Saxe-Coburg-Gotha during the First World War. The name "Windsor" refers to Windsor Castle - one of the main residences of the British monarch.
Monarchs of the Windsor dynasty.



King George VI in full dress.
since 1952: Elizabeth II.
Genealogy.
The Windsor dynasty is a British branch of the Saxe-Coburg-Gotha dynasty (and thus a branch of the House of Wettin), to which Queen Victoria's husband Prince Albert belonged (Victoria herself came from the Hanoverian dynasty).
The only king of Great Britain who belonged to the Saxe-Coburg-Gotha dynasty is officially considered Edward VII (reigned from 1901-1910).
From the point of view of traditional genealogy, in which kinship is considered through the male line, the Windsor dynasty should have ended with Elizabeth II.
Prince Charles and his descendants would have to belong to the Glücksburg branch of the House of Oldenburg, from which the husband of Elizabeth II Prince Philip comes (the Russian Emperor Peter III and all his descendants in the male line also belonged to this house). However, in view of the aforementioned 1952 proclamation, just as Russian tsars called themselves Romanovs, Charles and his descendants continue to be called Windsors.
The Oldenburgs are in Russia: the executed impostors: the "Romanovs", in Germany: the "Holstein-Gottorp", the Jews of Holstein, who in 1854 served the Prussian nobility together with the Jew Rothschild. Nikolaev Jewish soldiers of the old Red (Prussian) guard of Elston-Sumarokov.
The executed impostors of the Romanovs were not any "tsars" and even more so "Russians". They were Germans, bandits and ruffians. Just the same bandits as the Bolsheviks. For this they were shot. So, the reference to the executed impostors of the Romanovs (Jews of Holstein) is not appropriate, and for the Battenberg-Mountbattens it has shades of black humor. The Holstein-Gottorps ended badly in the Russia they captured.
George VI.

George VI (Eng. George VI, baptismal names Albert Frederick Arthur George; December 14, 1895, York Cottage, Sandringham, Norfolk, England - February 6, 1952, Sandringham) - King of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, Canada, Australia and South Africa since December 11, 1936. From the Windsor dynasty.
He ascended the throne after the abdication of his brother, Edward VIII. It went down in history primarily as a symbol of the struggle of Great Britain and the countries of the British Empire against Nazi Germany in World War II.
The reign of George is marked by the collapse of the British Empire and its transformation into the Commonwealth of Nations. He was the last emperor of India (from December 12, 1936 to August 15, 1947) and the last king of Ireland (until April 18, 1949). He bore the title of head of the Commonwealth of Nations (Eng. Head of the Commonwealth) from April 29, 1949.
That is, not the king. :(
On the father of Mary of Teck: Duke of Teck Farancisk - there is no data on the Internet. Although, it would seem: the oldest royal family. And some relatives are all either beggars, or impostors, or generally rootless people who could not be found for a hundred years. There is no data. This is strange.

Mary Adelaide Wilhelmina Elizabeth of Cambridge (Eng. Mary Adelaide Wilhelmina Elizabeth of Cambridge; November 27, 1833, Hanover - October 27, 1897, White Lodge, Richmond Park, London) - a member of the British royal family, granddaughter of George III. Daughter of Adolf Frederick, Duke of Cambridge and Augusta of Hesse-Kassel; wife of Francis, Duke of Teck and mother of Mary of Teck, Queen of Great Britain and Empress of India, wife of George V.
Mother-in-law is awesome! I like her! What you? Gorgeous!
Her paternal grandparents were King George V (1865-1936) and Queen Mary, Princess of Teck (1867-1953);
Lady Elizabeth Angela Marguerite Bowes-Lyon (Eng. Elizabeth Angela Marguerite Bowes-Lyon; August 4, 1900, London - March 30, 2002, Windsor) - wife of King George VI and mother of Queen Elizabeth II, queen consort of the United Kingdom in 1936-1952 as Queen Elizabeth (eng. Queen Elizabeth), the last Empress of India (1936-1950), Lord Keeper of the Five Harbors (1978-2002). Since 1952, she was known as Elizabeth Bowes-Lyon, not to be confused with the queen's daughter.
Bowes-Lyon, Claude George.

Claude George Bowes-Lyon, 14th Earl of Strathmore and Kinghorne - British aristocrat father of Elizabeth Bowes-Lyon, The Queen Mother, grandfather of Queen Elizabeth II.

Lord Charles Cavendish-Bentinck
by Lafayette (Lafayette Ltd)
sepia-toned proof print, 1900s
National Portrait Gallery, London
Claude was born in Lounds Square in the London Borough of Belgravia, the eldest of eleven children of Claude Bowes-Lyon, 13th Earl of Strathmore and Kinghorne, and his wife, Frances Dora Smith. One of his younger brothers, Patrick, was a tennis player and in 1887 won the Wimbledon doubles tournament.
After graduating from Eton College, Claude George was drafted into the 2nd Life Guards, where he served for six years until 1882. He was an active member of the Territorial Army and served as an honorary colonel in the 4th/5th Black Watch Battalion.
On the death of his father on February 16, 1904, he inherited the earldom and extensive estates in Scotland and England, including Glamis Castle. He was also appointed to the post of Lord Lieutenant of Angus, which he left in 1936 when his daughter Elizabeth became queen consort.
Claude George had a keen interest in forestry and was one of the first growers in the UK to grow larch from seed. On his estates, Bowes-Lyon had many small landowners and earned a brilliant reputation with his tenants. He was described by his contemporaries as an unassuming man who could often be seen wearing "an old mackintosh girded with a piece of fishing line". He worked on his lands and enjoyed manual labor on his estates. Visitors might mistake him for a simple worker.
Despite the earl's reserved attitude towards the royal family, in 1923 his youngest daughter married the second son of King George V, Prince Albert, Duke of York, and Lord Strathmore himself, to commemorate the marriage, was knighted in the Grand Cross of the Royal Victorian Order. Five years later, he was knighted in the Thistle.
In 1936, Edward VIII abdicated and his brother, Lord Strathmore's son-in-law, became king. As the father of the King's consort, Claude George was knighted in the Garter. Also, as a coronation award, in 1937 Bowes-Lyon was created Earl of Stutmore and Kinghorne in the Peerage of Great Britain, which allowed him to enter the House of Lords.
With age, Claude George began to rapidly lose his hearing. Lord Strathmore died of bronchitis on November 7, 1944 at the age of 89 at Glamis Castle.
Claude Bowes-Lyon, 13th Earl of Strathmore and Kinghorn "- the father of Elizabeth II's grandfather, from whom money, land and the title came to Elizabeth's grandfather: information on the Internet is missing. And this is the monarchy family of the Second (Third) Reich - Prussia on the whole planet. Also very strange. The origin is obtained from the lower (democratic) strata of the population of Greater Germany 1871-1946.
Born in Lounds Square in the London Borough of Belgravia, Claude was the eldest of eleven children of Claude Bowes-Lyon, 13th Earl of Strathmore and Kinghorne and his wife, Frances Dora Smith.
"Bose-Lyon, Francis" - information on the Internet is also missing . The origin of money, title and lands is not confirmed by the biographers of the English queen.
Elizabeth Angela Marguerite Bowes-Lyon was the youngest daughter and ninth of ten children of Claude George Bowes-Lyon (later 14th Earl of Strathmore and Kinghorne), and his wife Cecilia Nina Cavendish-Bentinck

Cecilia Nina Cavendish-Bentinck Countess of Strathmore and Kinghorne , and grandmother and godmother of Queen Elizabeth II.
Cecilia was born September 11, 1862 in the London Borough of Belgravia and was the eldest of three daughters of Charles William Frederick Cavendish-Bentinck and his second wife Caroline Louise Barnaby.
On July 16, 1881, Cecilia married the Scottish nobleman Claude George Bowes-Lyon (1855-1944) in Petersham. On the death of his father on 16 February 1904, Cecilia's husband inherited the earldom and extensive holdings in Scotland and England; Cecilia herself became Countess of Strathmore and Kinghorne.
Information on Elizabeth's maternal grandmother is also missing. But we are talking about the parents of Elizabeth I: the mother of Elizabeth II and the wife of George VI.
Cecilia Nina Cavendish-Bentinck, Countess of Strathmore and Kinghorne - September 11, 1862, London - June 23, 1938, ibid) - mother of Elizabeth Bowes-Lyon, the Queen Mother, and grandmother and godmother of Queen Elizabeth II.
But - the vaunted English aristocracy, lords, earls, rich people. Yes, and she was born in 1862, when photography in the United States was in full bloom. If photos of the parents of the English Queen Mother are not shown to anyone, then someone needs it. Simply put, they simply cannot be shown so as not to compromise the English royal family from the German occupiers of the Red Army of the Jewish Cossacks of Elston-Sumarokov.
The parents of the English Queen Mother Elizabeth II are not for you to arrange a theatrical show with Queen Victoria, this is a close time where stubborn journalists and paparazzi can unearth a true biography and make a scandal in the press worse than Diana Spencer and Camilla Parker-Bowles with Mr. Tampex.
If Philip's genealogy ends at great-grandfathers, then Elizabeth's is generally at her grandparents. Here you will inevitably post photographs of Queen Victoria in order to inspire your subjects with the idea of the great Hanoverian dynasty of good Germans of Saxe-Coburg-Gotha, in Russia: Holstein-Gottorp. And all together: the Jews of Holstein, who in 1854 served the Prussian nobility together with the Jew Rothschild.
For this, such an information curtain was needed from the impostors of the Romanovs, proteges of Germany, who were shot in Russia: the Jews of Holstein, who in 1854 served themselves the Prussian nobility together with the Jew Rothschild, so that they would not climb to check the genealogy of Elizabeth and Philip Battenberg on the Mountbatten's mother?
While everyone will be busy thinking about the photoshop of the good Germans Romanovs, in Germany: Holstein-Gottorp, Mountbattens and Rothschilds will quietly manage the captured centralized mega-state Czartoryski-Conde Army: Rome, Russia, Byzantium - the Novgorod Republic, the Federative State on the whole planet 1352- 1921
Democracy is called. The power of the Jews of the Rothschilds, who in 1854 served themselves the Prussian nobility together with the Jew Holstein (Romanov), in the Novgorod Republic of Russia captured by the red (Jewish) army - Rome - Byzantium on the banks of the Neva.

The date is incorrect. It is necessary for 1352 years less: in the summer of 567 from the Creation of the World (Rome, Russia, Byzantium, the Novgorod Republic) St. Michael the Archangel on the Palace Square of St. Petersburg-Petrograd-Leningrad.